This document covers 15 strategies and best-practices from around the world for storefront businesses and BIAs, to inspire and help you improve Ontario’s main streets.
Download the PDF here
Utilize Your Real Estate
>Brick-and-Mortar & E-Commerce Partnerships
Sell physical store products online; display online products in store. Online stores embrace physical stores, mainly by using the pop-up format, while main street stores have opportunities to collaborate with online stores.
Case Study: The “New Sephora Experience”’
>Retail Theatre Brick-and-Mortar Stores Are Transforming Into Showrooms
Retail Theatre is a display inside the store that is theatrical, artistic and creative and is deliberately designed to engage and entertain.
Case Study: Showfields SoHo
>Micro-Retail
Giant businesses move from superstores to smaller, demographically-targeted stores that focus on a small selection of popular products and aim to expose customers to the their products.
Case Study: Uniqlo Pop-Up
Change the Model
>Growing Pop-Up Partnerships
Pop-up stores are short-term, small-scale stores that are used to launch or market a new product. They are a platform for an online/offline strategy where the continuous change provides constant attraction.
Case Study: Recess, Manhattan, NYC
>Market-Style
Mostly applying for food & beverage, market-style retail allows visitors to enjoy a sit-down meal, shop for related products and recreate a dish at home. They also enjoy a wide variety of products from different booths.
Case Study: Eataly, Toronto
>Revenue & Profit Sharing With Landlords
Revenue and profit-sharing lease structures allow landlords and tenants to reduce risk while sharing the incentive for the success of the business.
Case Study: PanIQ Escape Room, Manhattan, NYC
Focus on the User Experience
>Social and Cultural Consciousness
Consumers are motivated by an unconscious emotional connection. They expect companies to engage consumers outside of the physical space and be cultural game-changers.
Case Study: Rent The Runway
>Experiential
Customers don’t just ‘shop’ anymore, espcially in main street stores. They seek a more engaging experience, as younger generations prefer exceptional experiences over things.
Case Study: ‘Neon Green’ by Louis Vuitton
>’Instagrammable’
Businesses can take advantage of Instagram and similar social media for exposure, by designing for aesthetic experiences that will be worth posting and sharing.
Case Study: The Vessel, Hudson Yards
Short-Term Experiments
>Engage with Transit Stops
Improve the waiting environment at bus/ streetcar stops through urban design and urban installations. Since transit is an integral part of the main street experience, improvements benefit not only riders but also the public realm and the businesses.
Case Study: Bus Stop Swing, Moscow
>Road Diet
A road diet, also called a lane reduction or road re-channelization, is a technique in transportation planning where the number of travel lanes and/or their width are reduced to improve safety and the pedestrian experience.
Case Study: ‘Measuring the Street’ by NYCDOT
>Interactive Urban Installations
Art installations that invite passersby to join in on a fun activity can transform even the most boring main street into a whimsical place. Art installations can be a cost-effective way to make the main street a destination for residents across the city.
Case Study: Impulse Installation, Montreal
Programming
>Playbourhoods
Turn the main street or parts of it into a place for play for young children, to attract children – and their parents.
Case Study: Playborhood.com
>Block Closure
Transforming a block or a few blocks into a neighbourhood event that brings residents together to socialize and experience their main street as a vibrant public space. Local organizations, families, neighbourhood associations and schools can also partner with the BIA.
Case Study: 8-80 Streets
>Weekly Market
A European model where small businesses can sell their products in a different location and setting. Weekly markets can attract residents from across the city while providing the locals with their ongoing needs.
Case Study: Ökomarkt am Kollwitzplatz, Berlin
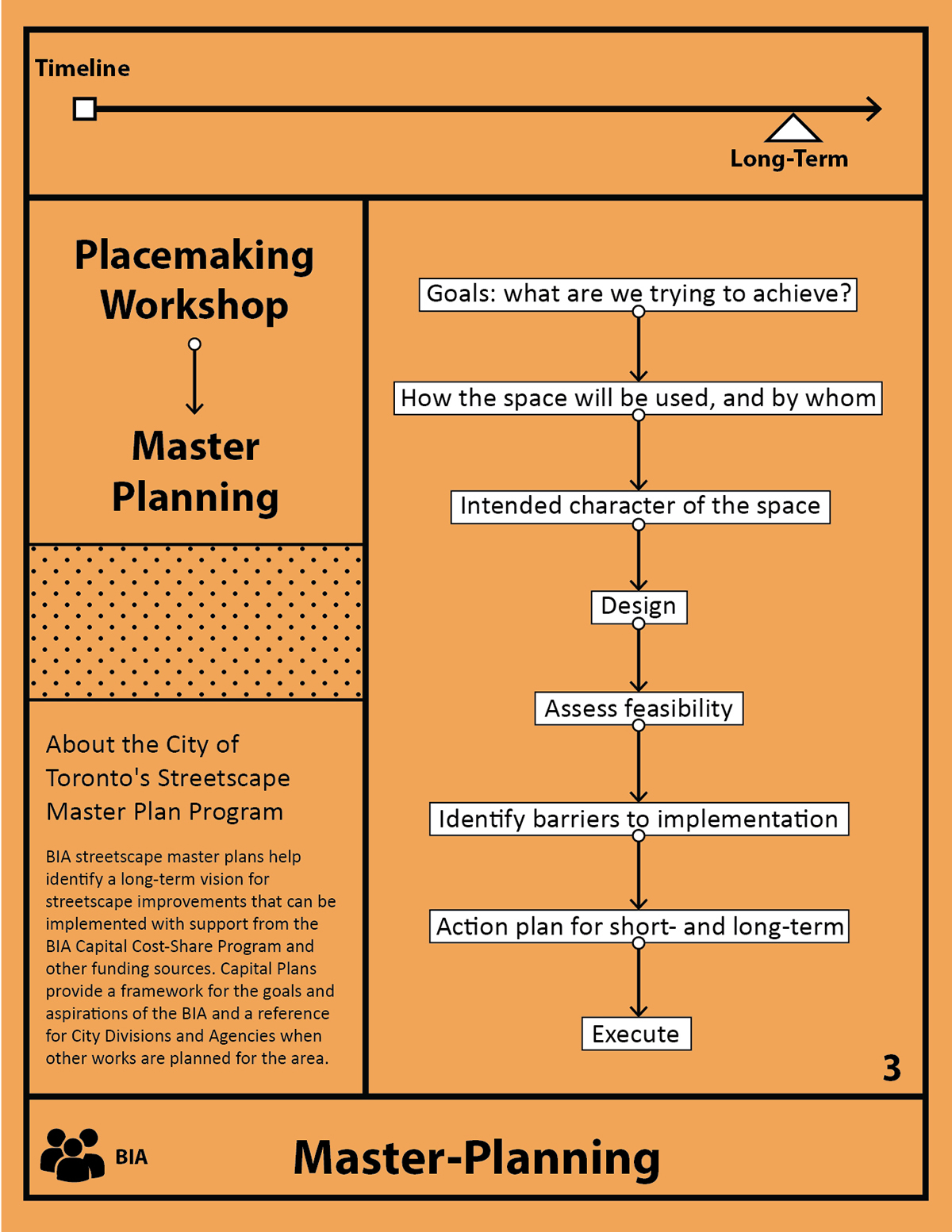
BIA Master-Planning